Mengenal Single Table Inheritance pada Rails (Contoh 1)
Table of Contents
Prerequisite
ruby 2.6.3 rails 5.2.4 postgresql 11.5
Prakata
Apa itu Single Table Inheritance?
Dapat didefinisikan sebagai tabel induk yang mewariskan sifat-sifatnya pada tabel anakan yang berelasi dengannya.
Ahahaha (^_^) definisi macam apa itu.
Abaikan.
Pada saat mengimplementasikan Single Table Inheritance (STI), saya menemukan lebih dari satu cara pada Rails. Maka dari itu, tulisan ini akan saya bagi dalam beberapa contoh.
Catatan kali ini adalah contoh pertama.
Kira-kira seperti ini ERD-nya.
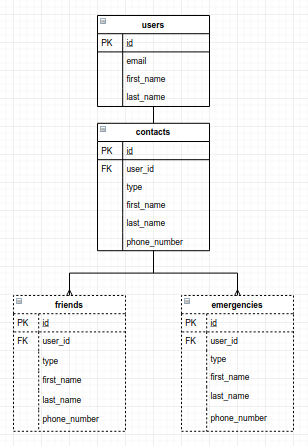
Gambar 1. ERD Single Table Inheritance contacts dengan friends dan emergencies
Migrations
Saya membuat dua buah model migration untuk tabel users dan contacts.
users
$ rails g model user email first_name last_name
!filename: db/migrations/20200219025008_create_users.rb
class CreateUsers < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.2]
def change
create_table :users do |t|
t.string :email
t.string :first_name
t.string :last_name
t.timestamps
end
end
end
contacts
$ rails g model contact user_id:integer type first_name last_name phone_number
!filename: db/migrations/20200219025125_create_contacts.rb
class CreateContacts < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.2]
def change
create_table :contacts do |t|
t.integer :user_id
t.string :type
t.string :first_name
t.string :last_name
t.string :phone_number
t.timestamps
end
add_index :contacts, [:type, :user_id]
end
end
Bagian penting yang harus ditambahkan adalah,
add_index :contacts, [:type, :user_id]
Kemudian jalankan migration tersebut.
$ rails db:migrate
Models
Setelah migration berhasil dijalankan, saya akan membuat scope pada model contact untuk model friend dan emergency.
!filename: app/models/contact.rb
class Contact < ApplicationRecord
scope :friends, -> { where(type: 'Friend') } # Contact.friends
scope :emergency, -> { where(type: 'Emergency') } # Contact.emergencies
end
Nah, kemudian tinggal buat kedua model tersebut.
!filename: app/models/friend.rb
class Friend < Contact
belongs_to :user
end
!filename: app/models/emergency.rb
class Emergency < Contact
belongs_to :user
end
Selanjutnya, model user yang memiliki relation has_many dengan kedua model tersebut.
!filename: app/model/user.rb
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_many :friends, class_name: 'Friend'
has_many :emergencies, class_name: 'Emergency'
end
Controllers
Model sudah jadi, selanjutnya mengatur controller.
Saya akan mulai dari users controller yang tidak perlu ada modifikasi.
!filename: app/controllers/users_controller.rb
class UsersController < ApplicationController
before_action :set_user, only: [:show, :edit, :update, :destroy]
# GET /users
def index
@users = User.all
end
# GET /users/1
def show; end
# GET /users/new
def new
@user = User.new
end
# POST /users
def create
@user = User.new(user_params)
if @user.save
redirect_to @user, notice: 'User was successfully created.'
else
render :new
end
end
# GET /users/1/edit
def edit; end
# PATCH/PUT /users/1
def update
if @user.update(user_params)
redirect_to @user, notice: 'User was successfully updated.'
else
render :edit
end
end
# DELETE /users/1
def destroy
@user.destroy
redirect_to users_url, notice: 'User was successfully destroyed.'
end
private
# Use callbacks to share common setup or constraints between actions.
def set_user
@user = User.find(params[:id])
end
# Only allow a list of trusted parameters through.
def user_params
params.require(:user).permit(:first_name, :last_name, :email)
end
end
Nah, selanjutnya contacts controller yang akan menggunakan object user di dalamnya.
!filename: app/controllers/contacts_controller.rb
class ContactsController < ApplicationController
before_action :set_contact, only: [:edit, :update, :destroy]
# GET /contacts/new
def new
@user = User.find(params[:user_id])
@contact = @user.send(set_type.pluralize).new
end
# POST /contacts
def create
@user = User.find(params[:user_id])
@contact = @user.send(set_type.pluralize).new(contact_params)
if @contact.save
redirect_to @user, notice: 'Contact was successfully created.'
else
render :new
end
end
# GET /contacts/1/edit
def edit; end
# PATCH/PUT /contacts/1
def update
if @contact.update(contact_params)
redirect_to @user, notice: 'Contact was successfully updated.'
else
render :edit
end
end
# DELETE /contacts/1
def destroy
@contact.destroy
redirect_to @user, notice: 'Contact was successfully destroyed.'
end
private
# Use callbacks to share common setup or constraints between actions.
def set_contact
@user = User.find(params[:user_id])
@contact = @user.send(set_type.pluralize).find(params[:id])
end
def set_type
case params[:type]
when 'Friend'
'friend'
when 'Emergency'
'emergency'
end
end
# Only allow a list of trusted parameters through.
def contact_params
params.require(set_type.to_sym).permit(
:user_id, :type, :first_name, :last_name, :phone_number, :address,
:city, :state, :birthday
)
end
end
Routes
Pada routes, saya akan menggunakan namespace untuk :users.
!filename: config/routes.rb
Rails.application.routes.draw do
root to: 'users#index'
resources :users do
resources :friends, controller: :contacts, type: 'Friend'
resources :emergencies, controller: :contacts, type: 'Emergency'
end
end
Dari routes tersebut, saya akan mendapatkan route seperti ini.
root GET / users#index
user_friends GET /users/:user_id/friends(.:format) contacts#index {:type=>"Friend"}
POST /users/:user_id/friends(.:format) contacts#create {:type=>"Friend"}
new_user_friend GET /users/:user_id/friends/new(.:format) contacts#new {:type=>"Friend"}
edit_user_friend GET /users/:user_id/friends/:id/edit(.:format) contacts#edit {:type=>"Friend"}
user_friend GET /users/:user_id/friends/:id(.:format) contacts#show {:type=>"Friend"}
PATCH /users/:user_id/friends/:id(.:format) contacts#update {:type=>"Friend"}
PUT /users/:user_id/friends/:id(.:format) contacts#update {:type=>"Friend"}
DELETE /users/:user_id/friends/:id(.:format) contacts#destroy {:type=>"Friend"}
user_emergencies GET /users/:user_id/emergencies(.:format) contacts#index {:type=>"Emergency"}
POST /users/:user_id/emergencies(.:format) contacts#create {:type=>"Emergency"}
new_user_emergency GET /users/:user_id/emergencies/new(.:format) contacts#new {:type=>"Emergency"}
edit_user_emergency GET /users/:user_id/emergencies/:id/edit(.:format) contacts#edit {:type=>"Emergency"}
user_emergency GET /users/:user_id/emergencies/:id(.:format) contacts#show {:type=>"Emergency"}
PATCH /users/:user_id/emergencies/:id(.:format) contacts#update {:type=>"Emergency"}
PUT /users/:user_id/emergencies/:id(.:format) contacts#update {:type=>"Emergency"}
DELETE /users/:user_id/emergencies/:id(.:format) contacts#destroy {:type=>"Emergency"}
users GET /users(.:format) users#index
POST /users(.:format) users#create
new_user GET /users/new(.:format) users#new
edit_user GET /users/:id/edit(.:format) users#edit
user GET /users/:id(.:format) users#show
PATCH /users/:id(.:format) users#update
PUT /users/:id(.:format) users#update
DELETE /users/:id(.:format) users#destroy
Views
Selanjutnya view template.
+ ...
- views/
- contacts/
_form.html.erb
edit.html.erb
new.html.erb
+ layouts/
- users/
- show/
_table_body.html.erb
_form.html.erb
edit.html.erb
index.html.erb
new.html.erb
show.html.erb
+ ...
Yang terpenting adalah users shows.
!filename: app/views/users/show.html.erb
...
...
<h1>Emergency Contacts</h1>
<%= link_to '+ New', new_user_emergency_path(@user) %>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>First Name</th>
<th>Last Name</th>
<th>Phone Number</th>
<th>Birthday</th>
<th>Action</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<% @user.emergencies.each do |contact| %>
<%= render 'users/show/table_body', user: @user, contact: contact %>
<% end %>
</tbody>
</table>
<h1>Friends Contacts</h1>
<%= link_to '+ New', new_user_friend_path(@user) %>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>First Name</th>
<th>Last Name</th>
<th>Phone Number</th>
<th>Birthday</th>
<th>Action</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<% @user.friends.each do |contact| %>
<%= render 'users/show/table_body', user: @user, contact: contact %>
<% end %>
</tbody>
</table>
Partial dari users/show/_table_body.
!filename: app/views/users/show/_table_body.html.erb
<tr>
<td><%= contact.first_name %></td>
<td><%= contact.last_name %></td>
<td><%= contact.phone_number %></td>
<td><%= contact.birthday %></td>
<td>
<%= link_to 'Edit', edit_user_emergency_path(user, contact) %> |
<%= link_to 'Delete', [user, contact], method: :delete %>
</td>
</tr>
Lalu form dari contacts/_form.
!filename: app/views/contacts/_form.html.erb
<%= form_with(model: [user, contact], local: true) do |form| %>
...
...
<% end %>
Yang perlu diperhatikan adalah pada bagian kedua partial di atas.
Terdapat [user, contact], karena contact merupakan controller namespace dan routing.
Oke, sepertinya segini aja.
Apaila teman-teman ingin melihat detail projectnya lebih jelas, ada di repository GitHub milik saya, di sini.
Mudah-mudahan dapat bermanfaat buat teman-teman.
Terima kasih.
(^_^)
Referensi
-
www.driftingruby.com/episodes/single-table-inheritance
Diakses tanggal: 2020-02-21 -
guides.rubyonrails.org/routing.html#controller-namespaces-and-routing
Diakses tanggal: 2020-02-21 -
api.rubyonrails.org/classes/ActiveRecord/Inheritance.html
Diakses tanggal: 2020-02-21
